In the modern world, thanks to the latest breeding developments, melons are grown not only in countries with a warm, dry climate, but also in risky farming areas, in greenhouse complexes, using the hydroponic method. However, the queen of all melons is rightfully considered to be the Central Asian variety Gulyabi. Due to the unique climatic conditions of this region, the Chardzhou variety is unsurpassed in terms of taste and melon culture.
History and characteristics of melon
Melon is an annual, photophilous, heat-loving plant, resistant to drought. It does not tolerate humid air, waterlogging of the soil, so the region of Central and Asia Minor is a priority in the cultivation of this gourd.
Selection
The Gulyabi melon variety was obtained by breeders in Turkmenistan (Chardzhou district), the Gulyabi orange variety was bred at the Uzbek Research Institute of Plant Production. Territory of growth - Central Asia, Kazakhstan.
Did you know? In the fruits of melon there are substances that, getting into the body, start the process of producing serotonin - the hormone of happiness.
Grade description
Currently, there are several subspecies of the Gulyaby variety:
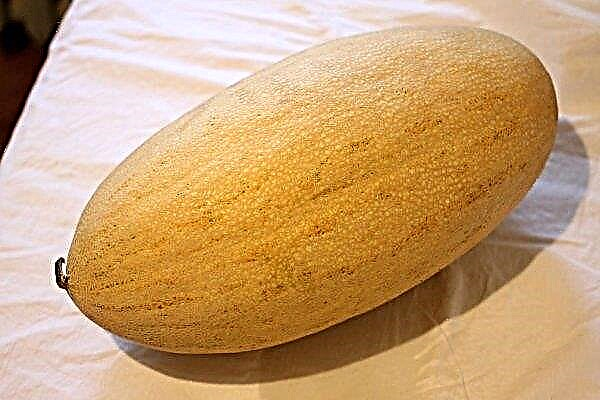
- Chardzhou melon (Gulyabi - green) - differs in smooth fruits without a "net" on the peel, juicy pulp, sweet as honey taste. Fruits weighing up to 7 kg. It is characterized by a long shelf life;
- Gulyaby-Chok - ovoid fruits with a thin orange peel. Pulp - sweet, oily, slightly astringent, with a honey aroma;

- Gulabi 803 - It is grown both in Turkmenistan and in Uzbekistan. Very dense bright yellow peel. The pulp is “crispy”, characterized by increased sugar content;

- Bosvaldi - medium-fruited variety (up to 5 kg) with fruits of almost green color, peel - tuberous to the touch. The pulp is white, closer to the peel it is light green, fibrous, juicy and sweet;

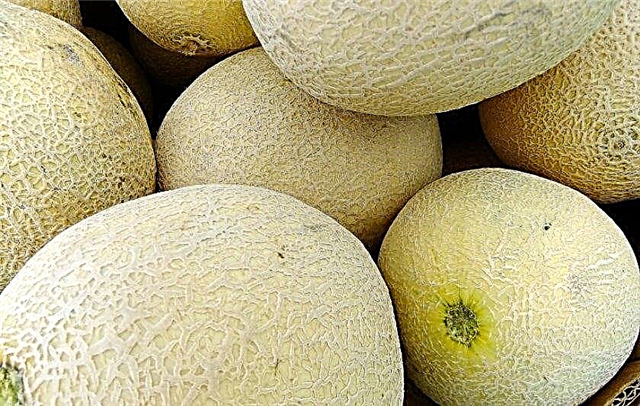
- Ghoul-walking - melons of this variety are distinguished by a large "mesh" pattern on a yellow-orange peel. Inside the fruit there is a uniform oily flesh with a high sugar content and a pronounced aroma.

Advantages and disadvantages
- The main advantages of Gulyabi melon:
- Very long shelf life without loss of consumer qualities.
- The ability to transport fruits over long distances.
- Widespread use in cooking: sweets, desserts, hot dishes, soups.
- Disadvantages:
- Demanding on climatic conditions: hot, arid climate during the entire ripening period - about 5 months.
- Absolutely does not tolerate moist air.
- The variety is not suitable for greenhouse cultivation.
Useful properties and harm
The positive characteristics of the Gulyabi melon include:
- Fruits contain almost all known vitamins, minerals and trace elements necessary for the full functioning of the human body.
- The melon pulp is rich in easily digestible sugars, so when it is consumed, it quickly saturates. It is recommended to use melon fruit as a therapeutic food for diseases of the joints, nervous and cardiovascular systems, to improve blood composition.
- Due to the microelement content of silicon, melon has a beneficial effect on the condition of the skin and hair.

The negative effects on the body include:
- Allergic reactions.
- Due to the high content of easily digestible sugars, melon is not recommended for patients with diabetes mellitus and people with impaired lipid metabolism.
- It is forbidden to use for bowel diseases.
- There is a possibility of excessive content of nitrate compounds.
Important! Dietitians recommend eating melon as an independent dish.
Gulyabi, Kolkhoznitsa and Torpedo: the difference
In addition to the fruits of the Gulyabi variety, such varieties as Kolkhoznitsa and Torpeda are widespread.
Their differences:
- If grade Gulyabi grows exclusively in the hot climate of Central Asia, the collective farmer is “born” from the Volga region and is currently widely distributed in Ukraine, Russia, Moldova.

- Collective farmer reaches its ripeness in early August. It is characterized by round, yellow fruits. It is worth noting that if the small size of Gulyabi and Torpedo speaks of insufficient ripeness of melons, then the melon of the Kolkhoznitsa variety with a diameter of 10 cm is a ripe fruit.

- Torpedo, like Gulyabi, it is grown in a hot climate, mainly in Uzbekistan, and reaches technical ripeness in late August. Her ripeness is judged by a large, very elongated fetus. The skin of the Torpedo should be yellow, without excessive brightness. The latter indicates an excess of nitrate compounds.

How to choose a ripe melon when buying
To understand whether a sweet melon or not, and choose the “right” fruit, you need to know a few secrets:
- The main criterion for choosing a melon is a bright, persistent vanilla-honey aroma. The ripened fruits of melon, unlike many fruits, exude a sweetish smell.
- Appearance of the melon: the peel is firm, without dents, cracks, or gross abrasions; when pressed, it should spring.
- The tail is dry, hard. If it is green, then the fruit was collected from the melon unripe.
- When you lightly hit the surface of a ripe melon, the sound comes out dull. If the sound is clear, the melon is not ripe.
Rules for landing in open ground
Despite the fact that melon is a southern culture and, therefore, very demanding on the temperature and humidity of both air and soil, many gardeners do not unsuccessfully grow this tasty and healthy fruit in their home gardens. Next, the main stages of growing melons in open ground will be described.
The timing
Melon seeds (optimal - three years ago) before planting are soaked for a short time in saline. Seeds that have surfaced on the surface of the solution are not suitable for further planting. Then it is washed several times with water and disinfection is carried out. For this, seed is placed in a saturated solution of potassium permanganate.
Depending on the spring weather conditions, landing in open ground must be made from the end of April to the end of May, provided that a stable warm temperature is established.
Important! The soil should be warmed not lower than + 13 ° С, air temperature should not fall below + 16 ° С.
Site selection
The main criteria for preparing the beds for planting:
- The bed for growing melons should be in a calm place, as drafts for the plant are destructive, and well lit.
- If in the previous season carrots, pumpkins or melons were grown on this site, this soil is not suitable for planting seeds.
- Optimum precursors are legumes, nightshade crops, garlic, onions.
- The soil for the cultivation of gourds should be permeable to prevent stagnation of water. This will be detrimental to plants.
- The soil on the bed is sandy, light, slightly saline with previously applied complex fertilizer (potassium, nitrogen, phosphorus) at the rate of 70 g / m².

Sowing technology
The sowing process is as follows:
- In prepared soil, 5 cm deep holes are made at a distance of about 80 cm from each other.
- The distance between the rows of holes is 1.5 m.
- Immediately before planting, each well is shed with warm water and several seeds are placed in it.
Care Tips
Subsequent care for gourds sown with seeds implies timely watering and top dressing, as well as the formation of bushes to get a better crop.
Watering
It should be watered exclusively along the grooves along the rows of holes with water heated to + 25 ° C. And only in the case when the soil has dried 5 cm in depth, as the ovaries form, plants are watered less often, and in the ripening phase, watering is completely excluded. Thus, the maximum sugar content is achieved in the fruits, and the plant itself avoids rot of both the root system and the terrestrial part.
Top dressing
For the entire period of growth, several fertilizing is carried out:
- The first top dressing is seven days after seed emergence. Fertilizers: Kemira, ammonium nitrate.
- The second top dressing is the period of active budding. Organic fertilizers: mullein solution or rotten bird droppings. Concentration 1:15.
- The third top dressing - three weeks after the second top dressing (overgrowth of ovary melon). Fertilizers: phosphorus and potash. Concentration: 50 g of phosphorus and 20 g of potash fertilizers are dissolved in a bucket of warm water.
Bushes
In order for the fruits to reach a conditional size by the time of harvesting, it is necessary to form the plant in time, otherwise the excess green mass will grow, and the fruits will not have time to finally form. To do this, pinch both side shoots, leaving three side and the main lash. Also, depending on the size of the fruit, it is necessary to remove the ovaries, leaving 2–5 pcs on the bush.
Soil care
Soil loosening is carried out exclusively in row-spacings. In the first month - until the rows of plants have closed to a distance between shoots of 15 cm, the next loosening is when the leaves close to 8 cm. After the plants grow to completely close to each other, the soil work is stopped.
Harvesting
Melon of Gulyabi variety is a late-ripening variety, fruits are harvested from melons in late August - early September.
Did you know? There are varieties of melons intended for the preparation of side dishes for meat. During the heat treatment of the melon pulp, salt and pepper are added.
There are several external signs by which you can determine whether it is ripe and tasty:
- in ripe fruit, the tail is uniformly dry;
- the end face of the fetus, where the flower was located, should be soft, but not pressed inward when the fetus is pressed;
- the skin color is evenly colored;
- the melon exudes a sweet aroma, and when you lightly hit the peel, a dull sound appears.
The Gulyabi melon variety is distinguished by long shelf life. Of particular note is the Chardzhou variety (Gulyabi green) - the fruits are stored until May of the year following the harvest. The exception is the Bosvaldi variety. Due to its very thin peel and loose pulp, it is not suitable for long-term storage and transportation over long distances. Melon is great as an independent dish, but it also goes well with dairy products (cocktails, creams, smoothies, casseroles), it is used to make jams, pastille, and fruit drinks. Melon is used in vegetable and fruit salads, dried in the sun, after which a valuable food product is obtained that retains the full composition of vitamins and minerals, which corresponds to fresh fruits.
Melon is great as an independent dish, but it also goes well with dairy products (cocktails, creams, smoothies, casseroles), it is used to make jams, pastille, and fruit drinks. Melon is used in vegetable and fruit salads, dried in the sun, after which a valuable food product is obtained that retains the full composition of vitamins and minerals, which corresponds to fresh fruits.




















