A household greenhouse is a great way to grow fruits, early vegetables and seedlings. It is pleasant to enjoy a tomato salad grown in your own greenhouse in early spring, for example, on March 8th.
Features of planting tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse
Many beginner gardeners are concerned about the optimal placement of beds in greenhouses. A summer resident with little experience may be confused, not knowing where to start, how to place seedlings of various varieties and requiring different growing conditions on a limited area of nutrition. In fact, there is nothing complicated, you need to start by installing a greenhouse, or rather, with the correct orientation to the cardinal points. It is best to install a greenhouse along the longitudinal east-west axis. In this case, all plants will receive the maximum stream of sunlight. In addition, the structure should be in an open area, tall trees or buildings, should not obscure the structure.
In fact, there is nothing complicated, you need to start by installing a greenhouse, or rather, with the correct orientation to the cardinal points. It is best to install a greenhouse along the longitudinal east-west axis. In this case, all plants will receive the maximum stream of sunlight. In addition, the structure should be in an open area, tall trees or buildings, should not obscure the structure.
Did you know? The largest greenhouse in the world, Eden, was built in England: its total area is 22,000 m², and the cost is about 135 million US dollars. A structure resembling a beehive, consisting of two domes, was built for 2.5 years.
Suitable width and height
The relatively small area of the greenhouse will not become an obstacle to growing a large number of different types of tomatoes: there is a place in the room to accommodate light-loving varieties, and those who like shade. Tall indeterminate species of tomatoes grow up, can reach two or more meters in length, respectively, and the greenhouse should be no less than the height.
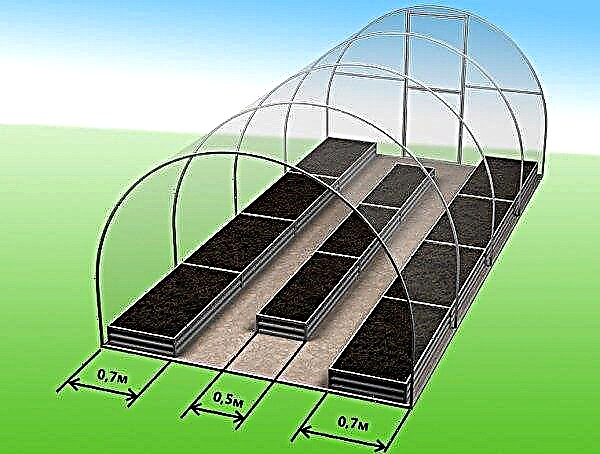
The dimensions of a typical greenhouse are 3 × 6 meters, and they allow you to make two options for the distribution of beds:
- 2 beds along the walls, the width of each bed is 1 m, with a central passage of the same width;
- 3 beds, 0.6 m wide (two along the walls, one in the center), with two aisles of 0.6 m;
- 3 beds (two lateral, 0.4 m wide, central 1 m) with two passes of 0.6 m. Moreover, the central bed does not reach the end wall by 0.6 m, resulting in a circular closed passage.
Important! Do not try to make the most of the internal space for the usable area, narrowing the aisles to a minimum and increasing the area of the beds. This will make it extremely difficult to care for the plants and, ultimately, will result in low process efficiency. In addition, narrow passages impede normal ventilation.
Protected soil beds
In the greenhouse, it is necessary to equip the beds. Depending on the region (south or north), as well as the purpose and characteristics of the beds (warm, for growing early vegetables), their height can range from 20-80 cm.
The sides themselves are usually made of such materials:
- wood - environmentally friendly, but short-lived material, does not like moisture, subject to debate, moreover, foci of pathogenic bacteria may appear in the pores;
- slate - the exact opposite of wood, with a long service life is far from the best option (from an environmental point of view);
- brick - takes up extra volume, installation requires effort and time.
Did you know? In Russia, they learned about tomatoes only in the XVIII century: then they were grown on flower beds, like flowers on which funny green formations grow. Only the work of agronomist Andrei Bolotov helped bring the process of growing tomatoes to their logical conclusion - the complete ripening of the fruit and harvest.
Quite recently, gardeners got acquainted with the modern original version of the sides for beds - a galvanized board. Without a doubt, the best option among those listed, which is equal to all characteristics, except for the price, no. The moisture of galvanizing is not terrible, as is the temperature difference. It is easy to carry out installation and dismantling, does not take up space, the fungus does not start in it
It is easy to carry out installation and dismantling, does not take up space, the fungus does not start in it
How to calculate the right amount of bushes
The next important point that should be decided: how many bushes of a particular variety can be planted in the greenhouse. Since the limited available space should maximize the use of the entire available area, without harming the plants, this issue should be taken very seriously.
Important! Do not use the greenhouse substrate in open ground - this can lead to an outbreak of diseases that previously were not in the garden.
The correct combination of different varieties (determinant with indeterminate, dwarf with high) will allow you to grow a fairly large crop. At the same time, tomatoes will not have difficulties with access of light and air, at the same time, the entire free volume will be effectively “loaded”.
Dwarf and undersized
Tomatoes, the height of the bush of which allows them to be attributed to dwarf or undersized varieties (up to about 80 cm), are planted 2 pieces in one hole. The planting pattern may vary, this will be discussed separately below, but the distance between the holes, in any case, should be within 0.4 m. After the seedlings have grown, thin out, removing weak shoots. With such a density of planting, you can place 160-200 bushes in a greenhouse
With such a density of planting, you can place 160-200 bushes in a greenhouse
Medium
Such bushes can reach 150-160 cm and above. Most often these are hybrids that are grown on ridges in two lines. The distance between the bushes is 45-55 cm. In this case, the greenhouse will grow to 45-50 bushes.
Tall
Tall hybrids (up to 1.8-2 m) are grown in a checkerboard pattern. In order for such large plants to grow and develop normally, they need an adequate living volume. So no more than 30-34 bushes are planted.
Spreading
Varieties and hybrids, which occupy a particularly large amount of space. They grow not only upwards, but also loop strongly enough. In order to create normal conditions for plants, no more than 12-14 bushes should be planted.
How to place tomatoes in a 3x6 m greenhouse
There are several factors that influence the placement of solanaceous plants in the greenhouse, the main of which are planting density and bush formation. In principle, these two factors are inextricably interconnected: their subsequent formation depends on how densely planted the plants are, and vice versa. The formation scheme of the tomato bush: a - single-stemmed plant; b - two-stemmed; c - three-stemmed; 1 - escape continuation; 2 - the main stalk For example, if a certain species is recommended to be grown in two stems, but the plants are planted too densely, you have to choose: either form a bush in one stalk or thin out, removing weaker seedlings and leaving strong with two stems.
The formation scheme of the tomato bush: a - single-stemmed plant; b - two-stemmed; c - three-stemmed; 1 - escape continuation; 2 - the main stalk For example, if a certain species is recommended to be grown in two stems, but the plants are planted too densely, you have to choose: either form a bush in one stalk or thin out, removing weaker seedlings and leaving strong with two stems.
Planting density
Density or density of crops - an indicator that gives an idea of the number of tomato bushes per unit area. Whether this value is correctly selected depends on how effectively you use the volume of the room. Too thick planting does not allow plants to grow normally: they lack air, nutrients, they prevent each other from growing, their vital activity turns into a struggle for existence.
For example, dwarf and undersized varieties grow in several stems. It is advisable to plant them in a staggered two-row order. The distance between the lines is at least 0.5 m, but more often - 0.65, between the bushes in the same row - 0.4 m. Standard and indeterminate hybrids are grown using the single-stem method, respectively, and these tomatoes can be planted denser, because one stem branches less than a few, and accordingly, it takes up less space. For such varieties, the distance between the lines is less - up to 0.5 m, between adjacent bushes - 0.35-0.4 m. Tomatoes of determinant hybrids need more free space - 0.65-0.7 m between the bushes and about 0, 45 m should be the distance between the lines.
Standard and indeterminate hybrids are grown using the single-stem method, respectively, and these tomatoes can be planted denser, because one stem branches less than a few, and accordingly, it takes up less space. For such varieties, the distance between the lines is less - up to 0.5 m, between adjacent bushes - 0.35-0.4 m. Tomatoes of determinant hybrids need more free space - 0.65-0.7 m between the bushes and about 0, 45 m should be the distance between the lines.
Rules for the formation of tomato bushes
The bush is formed depending on the type of tomato. Indeterminate hybrids are grown with one stem - it is strong enough and does not need additional lateral shoots. Determinant species are grown as a single-stem method, and in two stems. Such tomatoes stop growth, reaching a certain level. In addition, such species need to be tied. In general, tomatoes of this type require some care, for example, they need regular pinching, since excessive growth of lateral shoots has a bad effect on yield.You can say that giving determinant tomatoes the possibility of independent development, after a while you will see impenetrable thickets in the greenhouse, with large the number of very small fruits and the huge amount of green mass, the plant will spend all its strength and nutrients on the growth and maintenance of its vital activity.
In general, tomatoes of this type require some care, for example, they need regular pinching, since excessive growth of lateral shoots has a bad effect on yield.You can say that giving determinant tomatoes the possibility of independent development, after a while you will see impenetrable thickets in the greenhouse, with large the number of very small fruits and the huge amount of green mass, the plant will spend all its strength and nutrients on the growth and maintenance of its vital activity.
Schemes and technology of planting bushes
The correct planting scheme you have chosen will help not only get a decent tomato crop, but also greatly facilitate the care of plants. The most common crop planting patterns are double row and chess. There is also a combined one, some other schemes, but they are rarely used. The reason is simple: the two schemes completely satisfy the requirements of a particular type of vegetable crop, and their use greatly facilitates the work of the gardener, there’s no reason to come up with something new.
Double row
A simple and effective planting scheme, used, as a rule, for tomatoes with early ripening. As the name implies, it consists of two rows of plants, the distance between the rows is 0.7-0.75 m. The distance between two adjacent bushes in the same row is 0.5 m. You can say that you break your bed into rectangles, the long side of which (the distance between the rows) is located along the width of the greenhouse, and the short (the distance between adjacent bushes) is oriented along the length of the room. Tomatoes are planted in the corners of the rectangle.
You can say that you break your bed into rectangles, the long side of which (the distance between the rows) is located along the width of the greenhouse, and the short (the distance between adjacent bushes) is oriented along the length of the room. Tomatoes are planted in the corners of the rectangle.
Chess
Another name for this scheme is tape. The plants are arranged in the same two rows, with the difference that when viewed from above, the planting pattern is not like rectangles, as in the previous method, but like a broken line, a zigzag ribbon. The distance between the bushes is 0.5 - 0.7 m. The advantage of the method is more convenient care of plants and harvesting.
Tips from experienced gardeners
Some tips on growing tomatoes will help you get a plentiful harvest, as well as relieve the typical mistakes of beginning gardeners:
- perhaps now polycarbonate is the best material for greenhouses - it has low weight (no capital foundation is needed), it is easily mounted and dismantled, it has excellent technical characteristics, has an affordable price;
- room temperature, as well as the presence of drafts, depend on the direction of the wind. It follows that tomatoes that do not tolerate a sharp change in temperature should be planted near the walls of the room;
- An important growth factor for any plant is lighting. Varieties and hybrids that need more light are placed on the sunny side;
- in a limited space it is more expedient to grow varieties with different characteristics, combining and combining low-growing with high, light-loving and shade-loving. Thus, you can use the space to the maximum, creating all the plants necessary conditions for them;
- tall placed near the walls, undersized - closer to the aisles. This approach will not interfere with the care of tall bushes, you only need to reach out. At the same time, you will not need to reach for the low, making your way through the high, because they are nearby;
- in regions where spring weather is changeable and capricious, equip high, and better - warm beds;
- for growing early vegetables, or year-round, they build beds about 80 cm high. On the same beds vegetables are cultivated in a seedlingless manner;
- do not use fresh mullein for fertilizer - he burns out the root system of plants.
The correct use of agricultural techniques when growing plants in a greenhouse, as well as the timely introduction of the necessary fertilizing, are not all measures necessary to obtain a worthy crop. Equally important is to properly equip the greenhouse: this will help maximize the use of the entire useful volume of the room and facilitate your work.