An effective, but so far rarely used method of improving fertility is the use of green fertilizers (green manure). These are plants that are grown to improve soil composition. Everything is very simple by ear: sprinkle the earth with seeds, and when enough green mass has grown, dig up the earth. In practice, things are a little more complicated. Read about what and when to grow to increase potato yields in this review.
Basic rules for growing potatoes
Potato is a very productive crop that can grow on most soil types. Potatoes are unpretentious and require very little attention.
Did you know? The heaviest potato in the world is presented at the national gardening show in Somerset (UK) in September 2011. The weight of the potato was 4.98 kg.
Basic rules for growing:
- The root crop grows well on acidic soils (pH> = 7). Therefore, to add lime or other means of deoxidation of the soil in the area for growing is not necessary.
- Used organic fertilizers (manure) must be rotted. Autumn manure should be kept for at least 6 months before being introduced into the ground.
- Be sure to observe crop rotation. You can’t grow potatoes on the same site for several years in a row. You can return to the same site only after 3 years - this will avoid the accumulation of pests, fungi and other pathogens in the soil.
- Since the plant needs to develop roots (root tubers), a large amount of nitrogen is required with a gradual release. It can be urea, which contains up to 40% of slowly released nitrogen. It is introduced in the spring during planting.
- To feed potatoes with calcium and phosphorus, use bone meal or grass meal from alfalfa, seaweed, canola seeds.
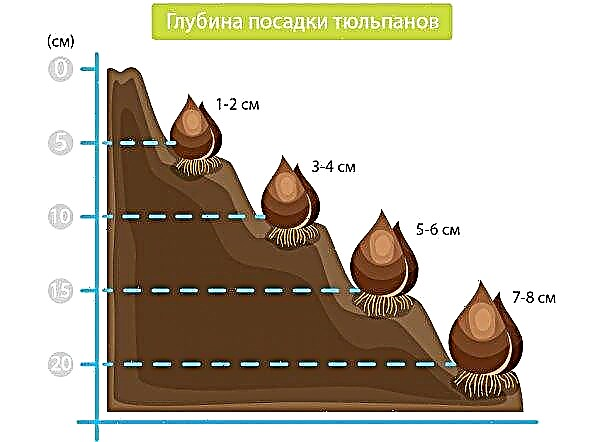
- When planting, potatoes are laid at the bottom of the trench to a depth of 30–40 cm at a distance of 40 cm from each other. Compost and fertilizers mixed with soil are laid on top. The soil layer above the potato should be at least 10 cm.
- After 6 weeks, when the tubers sprout, the layer is enlarged (they spud the potatoes) and cover the soil with mulch. Hilling is repeated monthly.
- Harvesting for food begins in mid-July. In September, after drying the tops, they dig up potatoes intended for winter storage.

Do siderates help produce potatoes
The Department of Plant Pathology at the University of Minnesota (USA) in 1991 conducted an experiment on the effect of green fertilizers on potatoes. The study lasted 2 years. We studied the effect of siderates on root diseases. In the course of the study, it was revealed that potatoes paired with buckwheat were much less likely to undergo vertical wilt. He also showed higher yields paired with buckwheat and canola.
Important! The timing of planting green manure depends on the purpose: to control pests, spring planting is used between rows, and to improve the structure of the soil — Autumn, after harvesting.
The same results were obtained in areas where potatoes were planted after alfalfa or corn. The soils on which cover crops grew were of significantly higher quality when growing other vegetables.
Functionally, the use of siderates is characterized by:
- an increase in the amount of organic fertilizers in the soil;
- improved aeration due to loosening of the soil by the root system;
- suppression of weed growth;
- soil erosion prevention;
- containment of verticillary wilting of potatoes and scab;
- attracting, along with beneficial insects, predator insects that destroy potato pests.
 The main principle of the action of green fertilizers is that planted plants extract nutrients from the soil and accumulate them in the roots and leaves - therefore fertilizers are called "green". When the green mass is immersed in the soil, it becomes a slowly released fertilizer.
The main principle of the action of green fertilizers is that planted plants extract nutrients from the soil and accumulate them in the roots and leaves - therefore fertilizers are called "green". When the green mass is immersed in the soil, it becomes a slowly released fertilizer.Choosing the best siderata for potatoes
Farmers divide siderates into 4 main groups:
- legumes;
- cereals;
- cruciferous;
- others.
To choose the best green fertilizers, you need to deal with the characteristics of each group.
- Legumes and lupins are annual herbs. They accumulate nitrogen from air and soil. Colonies of microorganisms grow and develop on their root system, which destroy putrefactive bacteria. Therefore, they are considered a good tool for the prevention of various diseases.

- Grain refers to winter rye or wheat. They are planted immediately after harvesting the main crop to improve soil composition. The root system of cereals makes the soil more loose.

- Mustard, rapeseed, colza belong to cruciferous. They are used both for winter sowing and for growing between rows. During flowering, they attract pollinating insects. And with them, predator insects appear on the beds, which destroy aphids and other pests that feed on plant sap.

- All other plant species that are used in the form of green manure belong to the fourth group.. A unique representative of this group is phacelia. She has the virtues of representatives of other groups and has no shortcomings. This beautiful frost-resistant honey plant, attractive to insects, can be grown between rows and used for crops in autumn.

Choosing siderata for sowing, you can use their combinations. The result is a kind of mixture of useful properties.
For planting potatoes recommend:
- legumes and lupins due to their ability to accumulate nitrogen. Clover will also be a good solution for this task;
- buckwheat, phacelia and rape to attract beneficial insects.
The effectiveness of other siderates may be equally high, but their side effects should be considered:
- Winter-hardy perennials form a powerful root system. Such a root system will continue to accumulate nutrients, taking them away from root crops.
- Some plants have the same pests as potatoes, and their planting will increase the number of pests, and not their destruction. To prevent this, pay attention to crop rotation rules and the family to which the selected plant belongs.

Landing time
Green fertilizer seeds can be sown from spring to fall. In the spring, planting is performed between rows - in this case, the task of plants is to protect potatoes from pests and attract beneficial insects. Beans, buckwheat, alfalfa are planted between the rows.
Important! The benefit of autumn planting of green fertilizers is that the plants do not have time to bloom, which means they will not have time to use the accumulated nutrients.
In autumn, planting is carried out to improve the soil composition for spring planting. Winter-hardy crops are planted at this time: rye, rape. But planting of herbaceous plants is also good, since the accumulated green mass during the winter will give nutrients to the soil, which is good for a future crop. Sow seeds in August or September, immediately after harvesting on the site.
What siderates to sow after harvesting potatoes
Rapeseed is in perfect harmony with potatoes. It is frost-resistant, tolerates frosts up to -7 ° C, and can be planted after harvest. Beans and alfalfa can also be planted in autumn. But farmers often grow mustard. It inhibits the development of the causative agent of verticillin wilt and reduces the number of soil pests, in particular, nematodes. It is also effective in controlling fungal pathogens and small seed weeds.
The mustard root system improves soil composition, retains nutrients in the roots and prevents them from going deeper into the soil, and also prevents soil erosion. In addition, mustard has the same pests as cabbage, which is considered a good precursor to potatoes in crop rotation.
Video: planting green manure after harvesting potatoes
What siderates are not suitable for potatoes
For the autumn planting of green fertilizers in temperate climates, rye and mustard are often used. These are cold-resistant crops that grow to the very frosts, and in warmer regions, and most of the winter. In the spring, the aboveground part of such crops is cut off with a plane cutter or lawn mower, and the main crop is planted on top of the tops.
Did you know? Every year, enough potatoes are grown around the world to completely cover the four-lane highway, which will wrap around the globe 6 times.
But rye is not recommended to be grown in front of potatoes due to the peculiarities of its root system. The roots of cereals germinate to a depth of 2 m. Cereals can be perennials, so their root system will absorb nutrients from the soil, but will not give them back to the main culture.
Features of planting potatoes after siderata
The root system of potatoes needs loose, well-drained soil with an acidity level of 5.0 to 7.0 pH. Fortunately, even in imperfect vegetation conditions, this root crop shows a good harvest. Soil temperature at the time of spring planting should not be lower than + 7 ° С. The soil should not be excessively wet. If ground cover plants were planted in the fall, the soil is dug up to a depth of 0.4 m and trenches are prepared for planting. The seized soil is piled next to the trench. Correctly will form a kind of layer cake:
Correctly will form a kind of layer cake:
- At the bottom of the trench, 7-10 cm of loose soil is placed.
- Potatoes are laid on top.
- Root crops are covered with a layer of soil with fertilizers 10 cm high.
- A layer of ordinary soil is added on top.
The remaining soil near the trench will be needed for hilling potatoes in 6 weeks. Thus, you can opt for any siderat plants from the extensive list. Their effectiveness is a scientifically proven fact. In addition, their use in most cases does not have side effects or contraindications.